Although this blog is not about what a Motherboard is, we’ll take a recap, and define a Motherboard. A motherboard is basically a printed circuit board (PCB) used to connect different parts of a computer like the central processing unit, memory, hard drive, printer, mouse, keyboard, graphics card, and other peripherals through physical slots and interface connectors.
We have a blog about Motherboards, please check it out.
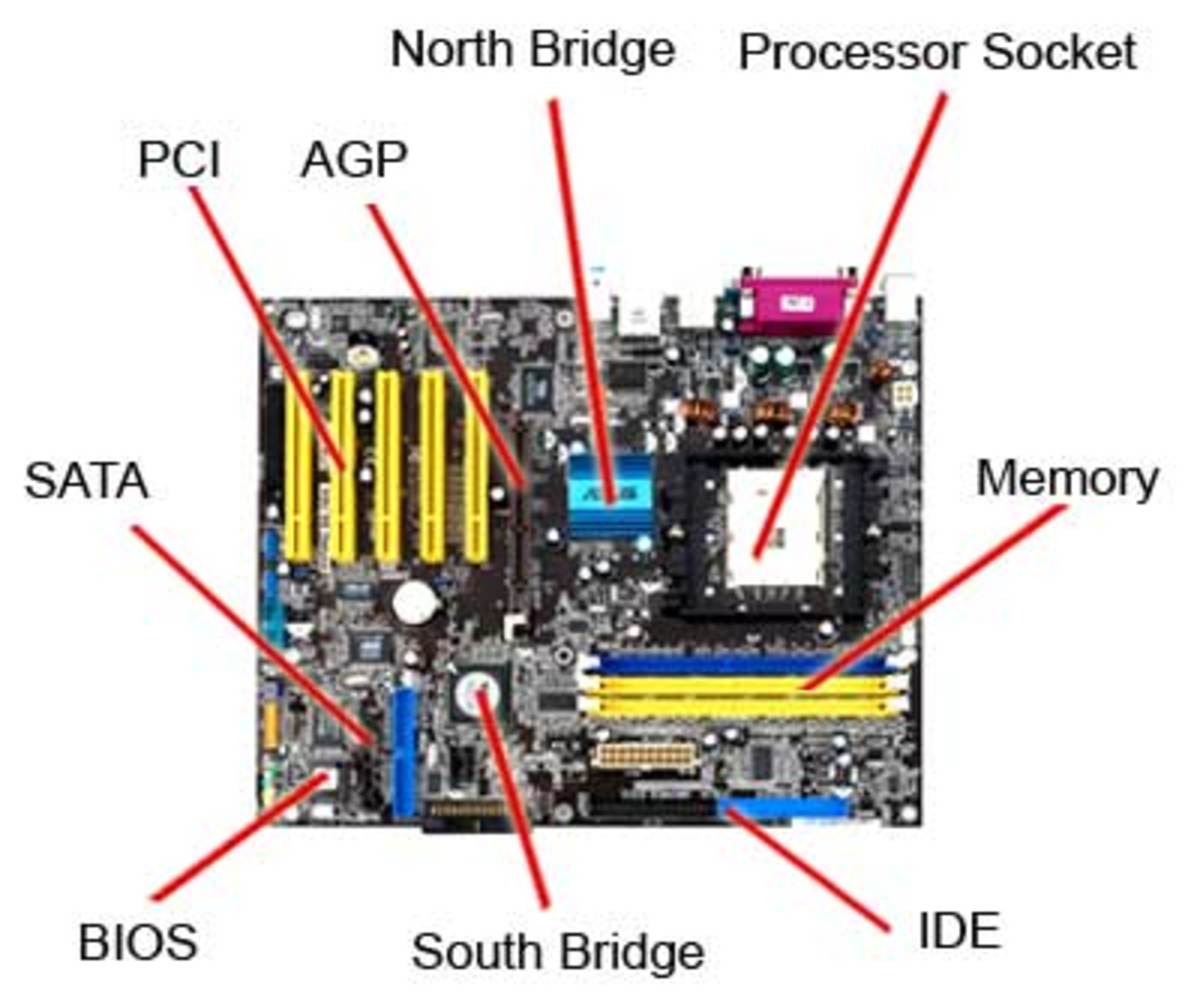
What are the parts of a Motherboard?
1. BIOS And CMOS
2. Input/Output Ports
3. IDE And SATA Connector (Storage Device Connectors)
4. Power Connectors
5. Front I/O Connectors
6. CPU Socket
7. Expansion Card Slots
8. RAM (Memory) Slots
9. M.2 Slot
1. BIOS And CMOS: BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. BIOS is a "read-only" memory, which consists of low-level software that controls the system hardware and acts as an interface between the operating system and the hardware. BIOS stands for Basic Input/Output System. BIOS is a "read-only" memory, which consists of low-level software that controls the system hardware and acts as an interface between the operating system and the hardware. Motherboards also include a small separate block of memory made from CMOS RAM chips which are kept alive by a battery (known as a CMOS battery) even when the PC’s power is off. This prevents reconfiguration when the PC is powered on.
2. Input/Output Ports: Also commonly referred to as I/O ports for short. These ports are located at the back of the computer and are often color-coded. Examples of ports include microphones, Speakers and Headphones, Headsets, Earbuds, etc.
3. IDE And SATA Connector: IDE is an interface standard for the connection of storages devices such as Hard Disk Drives (HDD), Solid State Drives (SSD) and CD/DVD drives to the computer. SATA is a computer bus interface or standard hardware interface which connects connecting hard drives, Solid State Drives (SSD) and CD/DVD drives to the computer
4. Power connectors: Power connectors are devices that allow an electrical current to pass through it for the exclusive purpose of providing power to a device. Although it comes in all shapes and sizes and with various abilities, options, and accessories, the purpose of a power connector always comes back to one all-important thing: power.
5. Front I/O Connectors: This is where you connect the Power Switch, LED power indicator, Reset Switch, and HDD LED cables. The front audio port and front USB are also connected here. These connections are usually located at the bottom part of the motherboard
6. CPU Socket: A CPU socket uses a series of pins to connect a CPU’s processor to the PC’s motherboard. If a CPU is connected via a CPU socket, it is not soldered and can therefore be replaced. CPU sockets are more common with desktop gaming PCs than they are on laptops.
7. Expansion Card Slots: The expansion card slots are where you add extra components such as a video card, network card, audio card, or PCIe SSD. The slots are located in the bottom half of the motherboard below the CPU socket.
8. RAM: RAM, or Random-Access Memory, slots are one of the most important parts of a motherboard. The RAM slots are, unsurprisingly, where you place the RAM modules. There is the SIMM slot (Single in-line memory module) that only supports a 32-bit bus, and there is the DIMM slot (Dual inline memory module) that can simultaneously run with a 64-bit bus.
9. M.2 SLOT: M.2 is a form factor for SSDs (solid-state drives) that’s shaped like a stick of gum. These SSDs are generally faster but more expensive than traditional, 2.5-inch SSDs.
Would you like to learn more about how motherboards work? click here.
 Share
Share